Uterine fibroids are common noncancerous growths that can cause significant discomfort and impact a woman’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available. This article explores the most effective treatment for uterine fibroids, including non-surgical and minimally invasive procedures.

What Are Uterine Fibroids? 🤔
Uterine fibroids are benign uterine growths, often during a woman’s reproductive years. These growths, also known as fibroid tumours, leiomyomas, or fibroids, comprise muscle and fibrous tissue. Although noncancerous, fibroids can cause significant discomfort and complications for many women. The size, location, and number of fibroids vary, and some women may not even realise they have them, while others may experience severe symptoms.
What Are the Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids? 📋
The symptoms of uterine fibroids can vary greatly depending on the size, location, and number of fibroids. Common symptoms include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Abdominal swelling
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Painful intercourse
- Prolonged or irregular periods
- Back or leg pain
In severe cases, fibroids may also lead to anemia due to excessive bleeding. However, not all women with fibroids experience symptoms and the severity of the symptoms often depends on the size and location of the fibroid(s).
What Causes Uterine Fibroids? 🔬
The exact cause of uterine fibroids is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to play a role in their development:
- Hormonal fluctuations: Estrogen and progesterone, two hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, are known to stimulate fibroid growth. Fibroids tend to shrink after menopause when hormone levels decrease.
- Genetic factors: There is a vital hereditary component to fibroid development. Women with a family history of fibroids are more likely to develop them.
- Other factors: Obesity, early menstruation, and a diet high in red meat and low in green vegetables, fruit, and dairy may also increase the risk of developing fibroids.
☑️ How do you know if you have uterine fibroids?
Types of Uterine Fibroids 📌
There are different types of fibroids, classified based on their location within the uterus:
- Intramural fibroids: Located in the muscular wall of the uterus, these are the most common type.
- Subserosal fibroids: These grow on the outer wall of the uterus and may cause pressure on surrounding organs like the bladder.
- Submucosal fibroids: Found under the uterus lining, they can affect the menstrual cycle and are often associated with heavy bleeding.
- Pedunculated fibroids grow on stalks inside or outside the uterus, resembling a mushroom-like structure.
The best treatment for uterine fibroids depends on various factors, including the size, location, and number of fibroids, the severity of symptoms, the patient’s age, overall health, and whether the patient wishes to preserve fertility. Here are some of the most effective treatment options:
Which is best treatment for uterine fibroids?
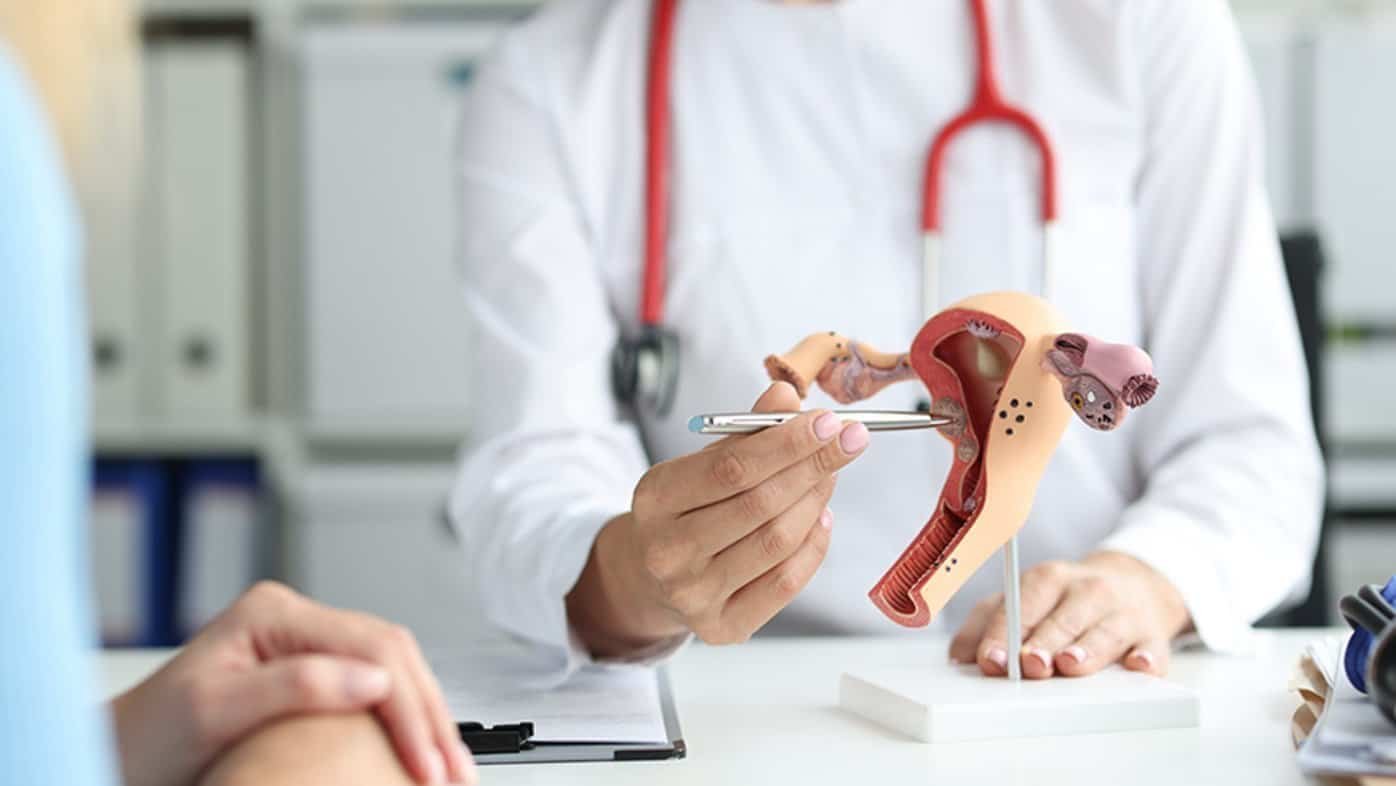
Choosing the treatment of uterine fibroids depends on various factors, including the size, location, and number of fibroids, the severity of symptoms, the patient’s age, overall health, and whether the patient wishes to preserve fertility. Below are some of the most effective treatments available:
Uterine artery embolization (UAE)
- Best For Women seeking a non-surgical option to preserve their uterus.
- How It Works: UFE is a minimally invasive procedure that blocks the blood supply to the fibroids, causing them to shrink over time. This procedure is highly effective, with a quick recovery period, and is particularly suited for women who want to avoid surgery.
- Benefits: No surgery is required, recovery time is shorter, the uterus is preserved, and there is significant symptom relief.
MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound Surgery (MRgFUS)
- Best For Women preferring a completely non-invasive treatment.
- How It Works: This procedure uses high-intensity ultrasound waves to destroy fibroid tissue, guided by MRI imaging. It’s an outpatient procedure with no incisions, making it a safe and effective option.
- Benefits: Non-invasive, no hospital stay required, quick recovery, and effective in reducing symptoms.
Myomectomy
- Best For Women looking to preserve their fertility through a surgical option.
- How It Works: Myomectomy involves surgically removing fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. It can be performed via traditional open surgery, laparoscopic, or robotic surgery, depending on the size and location of the fibroids.
- Benefits: Effective in removing fibroids, preserving fertility, and providing symptom relief.
Hysterectomy
- Best For: Women who no longer wish to have children and seek a permanent solution.
- How It Works: Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus, providing a definitive cure for fibroids by eliminating the possibility of recurrence.
- Benefits: Permanent relief from fibroid symptoms, no recurrence, is often recommended when other treatments have failed or fibroids are enormous.
Medications
- Best For Women with mild symptoms or those seeking short-term relief.
- How It Works: Medications, such as GnRH agonists, progestin-releasing IUDs, or anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, can help manage symptoms like heavy bleeding and pain. These may also shrink fibroids temporarily.
- Benefits: Non-invasive, helps manage symptoms, and often serves as a temporary solution or preparation for surgery.
Radiofrequency Ablation
- Best For Women seeking a minimally invasive procedure with quick recovery.
- How It Works: This procedure uses heat to destroy fibroid tissue and is typically performed laparoscopically, meaning fewer incisions and a faster recovery time.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive, effectively reducing symptoms, and preserves the uterus.
Uterine Fibroid Supportive Therapy
Supportive therapy for uterine fibroids involves non-surgical methods aimed at managing symptoms and improving quality of life without directly treating the fibroids themselves. These therapies are often used when fibroids are small or when surgery is not immediately necessary. Below are common supportive treatment options for uterine fibroids:
1. Pain Management:
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs): Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with fibroids.
- Hormonal Contraceptives: Birth control pills, patches, or intrauterine devices (IUDs) with hormones can help regulate menstrual cycles, reducing heavy bleeding and cramping.
2. Hormonal Therapies:
- GnRH Agonists (Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Agonists): Medications like leuprolide can temporarily shrink fibroids by lowering estrogen and progesterone levels. However, these are usually short-term options due to side effects like bone thinning.
- Progestin-Releasing IUDs: These can help reduce heavy menstrual bleeding and provide contraception while managing fibroid symptoms.
3. Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in red meats may help reduce symptoms, though more research is needed.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall health and reduce stress, which may help manage fibroid symptoms like pain and discomfort.
4. Iron Supplements:
- If fibroids cause heavy menstrual bleeding, iron supplements can help prevent or treat anemia resulting from blood loss.
5. Herbal and Natural Remedies:
- Some women use herbal supplements like green tea extract or Chinese herbal medicines to alleviate symptoms, but it’s important to consult with a doctor before trying these alternatives.
6. Psychological Support:
- Therapy and Support Groups: Coping with fibroid symptoms can be stressful. Joining support groups or seeking counseling can help manage emotional well-being.
7. Heat Therapy:
- Heating Pads or Hot Water Bottles: Applying heat to the abdomen can help reduce cramps and discomfort.
These therapies do not remove fibroids but can help control symptoms, such as pain, heavy bleeding, and pressure on other organs. For individuals looking for more permanent solutions, interventional treatments like uterine artery embolization or surgical options (e.g., myomectomy or hysterectomy) may be considered.
Risks to uterine fibroid treatment
treatment for uterine fibroids involves a variety of procedures and medications, each carrying its own set of risks and potential complications. Here are some critical risks associated with different treatment options:
Surgical Risks
- Myomectomy (fibroid removal): Although effective, this surgery carries risks such as bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissue. Laparoscopic and robotic approaches reduce recovery time but still involve risks associated with any surgery.
- Hysterectomy: This is a significant surgery that permanently removes the womb. Risks include infection, heavy bleeding, and long-term complications such as hormone imbalance if the ovaries are also removed.
- Laparotomy: An open surgery to remove large fibroids, which carries a longer recovery time and higher risks of infection and bleeding.
- Minimally Invasive Procedure Risks
- Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE): While generally safe, UFE can cause post-procedure pain, infection, or premature menopause. There’s also a small risk that the procedure may not shrink the fibroids enough to relieve symptoms.
- MRI-Guided Focused Ultrasound (MRgFUS): This noninvasive treatment carries fewer risks, but there’s a possibility of incomplete treatment, leading to persistent symptoms.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (Acessa): In this procedure, heat is used to destroy fibroid tissue, but there’s a risk of damage to nearby organs and tissues, as well as incomplete fibroid destruction.
Medication Risks
- Hormonal Therapies: GnRH agonists and ulipristal acetate can be effective in reducing fibroid size, but they may cause side effects such as hot flashes, bone loss, and mood changes. Long-term use is generally not recommended.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and other NSAIDs can help manage pain but may cause gastrointestinal issues if used frequently.
- Progestin-releasing IUDs: While helpful in controlling heavy menstrual bleeding, these devices can cause irregular bleeding and other side effects.
General Risks
- Impact on Fertility: Some treatments, particularly surgical ones like hysterectomy, eliminate the possibility of future pregnancies. Others, like UFE, may reduce fertility or complicate future pregnancies.
- Incomplete Symptom Relief: Some treatments might not fully relieve symptoms or require additional procedures if fibroids recur or are not fully treated.
FAQS
How to Check for Fibroids at Home?
While a definitive diagnosis of uterine fibroids requires a medical examination, there are some signs you can monitor at home. Symptoms of fibroids often include heavy menstrual periods, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, and frequent urination. If you notice these signs, scheduling a visit with your doctor is essential. However, self-checking for fibroids at home is limited, as fibroids are typically detected through imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI, often performed by trained professionals. If you’re experiencing symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider is the best action to ensure proper diagnosis and care.
Which Size of Fibroid Is Dangerous?
The size of a fibroid alone doesn’t necessarily determine its danger, but larger fibroids can cause more significant health issues. Typically, fibroids more prominent than 5-10 cm are considered more concerning, mainly if they cause severe symptoms. Here’s how size can impact the severity:
- Large Fibroids (over 5 cm): These can cause abdominal distention, painful periods, heavy menstrual bleeding, and pressure on surrounding organs like the bladder or bowels, leading to urinary or digestive issues.
- Very Large Fibroids (over 10 cm): These can lead to significant complications, including a higher risk of complications during pregnancy and potential obstruction of the birth canal. Such fibroids may also cause severe pelvic pain and pressure, making them more dangerous.
- Pedunculated Fibroids (on a stalk): Regardless of size, if these fibroids twist, they can cut off their blood supply, leading to acute pain and requiring immediate medical attention.
Can Fibroids Be Treated Without Surgery?
Yes, fibroids can often be treated without surgery. Several non-surgical options are available, including:
- Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE): A minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting small particles into the artery supplying the fibroids, which blocks their blood flow and causes them to shrink.
- Medications: Hormonal treatments such as GnRH agonists, ulipristal acetate, and progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs) can help manage symptoms by reducing fibroid size and controlling menstrual bleeding.
- Focused Ultrasound Therapy: This noninvasive treatment uses ultrasound waves to heat and destroy MRI-guided fibroid tissue.
- Endometrial Ablation: A procedure that destroys the endometrial lining of the uterus, which can reduce menstrual bleeding associated with fibroids.
These treatments are especially beneficial for women who want to avoid surgery or are not candidates for surgical procedures.
What Size Fibroids Need Surgery?
The decision to recommend surgery for fibroids often depends on a combination of size, location, and the severity of symptoms rather than size alone. However, large fibroids (typically over 5-10 cm) that cause significant symptoms such as heavy bleeding, pain, or pressure on other organs often require surgical intervention. Surgical options include:
- Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids, often recommended for women who wish to preserve fertility.
- Hysterectomy: The complete removal of the uterus, which is a permanent solution for fibroid-related issues.
What Is the Fastest Way to Cure Fibroids?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the fastest way to “cure” fibroids, as treatment depends on individual circumstances, including the size, location, and symptoms of the fibroids and the patient’s reproductive plans. However, for rapid symptom relief:
- Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) offers quick symptom relief by causing fibroids to shrink and reduce size.
- GnRH agonists can temporarily shrink fibroids within a few weeks but are typically used as a short-term solution.
- Surgical options like myomectomy or hysterectomy offer definitive results but involve recovery time.
Each treatment’s speed and effectiveness will vary, so it’s essential to consult with a medical professional or gynecologist to determine the best treatment plan for your specific situation.
Conclusion
Each treatment option for uterine fibroids offers benefits but also carries potential risks. It’s essential to discuss these risks with a qualified healthcare provider or gynecologist to determine the best and safest option for your individual needs. Always consider factors like age, desire for future pregnancies, and overall health when deciding on a treatment plan.
☑️ Finding the Best Fibroid Specialist in London: Dr. Samir Abdel Ghaffar

 العربية
العربية